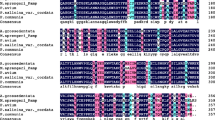
Abstract
Two cultivars of Perilla frutescens, red and green formas, are known to differ in anthocyanin accumulation in leaves and stems. cDNA clones encoding the enzymes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis, chalcone synthase (CHS), flavanone 3-hydroylase (F3H), dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR), and UDP glucose: flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase (3GT), were isolated from cDNA libraries derived from the leaves of a red forma of P. frutescens by screening with partial fragments amplified by means of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and heterologous cDNAs as probes. The deduced amino acid sequences of these four genes exhibited 40–90% identity with those reported for the corresponding gene from other unrelated species. Southern blot analysis for these genes and two other structural genes, the leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX, anthocyanidin synthase) and anthocyanin acyltransferase (AAT) genes, indicated that each gene comprises a small multi-gene family. More than three copies of the CHS gene are present, two copies of the other genes being present. The expression of five genes, the exception being the CHS gene, was detected only in red leaves of the red forma of P. frutescens, i.e. not in green leaves of the green forma plant. The CHS gene was expressed in both red and green leaves, but 10-fold more in red leaves than in green leaves. These results suggest that the expression of all structural genes examined is coordinately regulated in a forma-specific manner. Under weak-light conditions, the accumulation of both anthocyanin and mRNAs of biosynthetic enzymes was lower in leaves of the red forma. High-intensity white light coordinately induced the accumulation of transcripts of all six genes examined in the mature leaves of red P. frutescens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beld M, Martin C, Huits H, Stuitje AR, Gerats AGM: Flavon oid synthesis in Petunia hybrida: partial characterization of dihydroflavonol-4-reductase genes. Plant Mol Biol 13: 491– 502 (1989).
Bongue-Bartelsman M, O'Neill SD, Tong Y, Yoder JI: Characterization of the gene encoding dihydroflavonol 4-reductase in tomato. Gene 138: 153–157 (1994).
Boss PK, Davies C, Robinson SP: Expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway genes in red and white grapes. Plant Mol Biol 32: 565–569 (1996).
Britsch L, Dedio J, Saedler H, Forkmann G: Molecular characterization of flavanone 3β-hydroxylases. Consensus sequence, comparison with related enzymes and the role of conserved histidine residues. Eur J Biochem 217: 745–754 (1993).
Britsch L, Ruhnau-Brich B, Forkmann G: Molecular cloning, sequence analysis, and in vitro expression of flavanone 3β-hydroxylase from Petunia hybrida. J Biol Chem 267: 5380– 5387 (1992).
Chandler VL, Radicella JP, Robbins TP, Chen J, Turks D: Two regulatory genes of the maize anthocyanin pathway are homologous: isolation of B utilizing R genomic sequences. Plant Cell 1: 1175–1183 (1989).
Christie PJ, Alfenito MR, Walbot V: Impact of low-temperture stress on general phenylpropanoid and anthocyanin pathways: Enhancement of transcript abundance and anthocyanin pigmentation in maize seedlings. Planta 194: 541–549 (1994).
Cone KC, Burr FA, Burr B: Molecular analysis of the maize anthocyanin regulatory locus C1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 9631–9635 (1986).
Cone KC, Cocciolone SM, Burr FA, Burr B: Maize anthocyanin regulatory gene pl is a duplicate of c1 that functions in the plant. Plant Cell 5: 1795–1805 (1993).
Consonni G, Geuna F, Gavazzi g, Tonelli C: Molecular homology among members of the R gene family in maize. Plant J 3: 335–346 (1993).
Deboo GB, Albertsen MC, Taylor LP: Flavanone 3-hydroxylase transcripts and flavonol accumulation are temporally coordinate in maize anthers. Plant J 7: 703–713 (1995).
Dooner HK, Robbins TP, Jorgensen RA: Genetic and developmental control of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet 25: 173–199 (1991).
Franken P, Niesbach-Klösgen U, Weydemann U, Maréchal-Drouard L, Saedler H, Wienand U: The duplicated chalcone synthase genes C2 and Whp (white pollen) of Zea mays are independently regulated: evidence for translational control of Whp expression by the anthocyanin intensifying gene in. EMBO J 10: 2605–2612 (1991).
Goodrich J, Carpenter R, Coen ES: A common gene regulates pigmentation pattern in diverse plant species. Cell 68: 955–964 (1991).
Gould KS, Kuhn DN, Lee DW, Oberbauer SF: Why leaves are sometimes red. Nature 378: 241–242 (1995).
Frohnmeyer H, Ehmann B, Kretsch T, Rocholl m, Harter K, Nagatani A, Furuya M, Batschauer A, Hahlbrock K, Schäfer E: Differential usage of photoreceptors for chalcone synthase gene experssion during plant development. Plant J 2: 899–906 (1992).
Harborne JB: The Flavonoids: Advances in Research since 1986, pp. 449–564. Chapman & Hall, London (1993).
Helariutta Y, Elomaa P, Kotilainen M, Seppänen P, Teeri TH: Cloning of cDNA for dihydroflavonol-4-reductase (DFR) and charaterization of dfr expression in the corollas of Gerbera hybrida var. Regina (Compositae). Plant Mol Biol 22: 183– 193 (1993).
Holton T, Cornish EC: Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7: 1071–1083 (1995).
Hopp TP, Woods KR: Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 3824–3828 (1981).
Huits HSM, Gerats AGM, Kreike MM, Mol JNM, Koes, RE: Genetic control of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene expression in Petunia hybrida. Plant J 6: 295–310 (1994).
Koes RE, Spelt CE, Mol JNM: The chalcone synthase multigene family of Petunia hybrida (V30): differential, light-regulated expression during flower development and UV light induction. Plant Mol Biol 12: 213–225 (1989).
Koes RE, Spelt CE, Reif HJ, van den Elzen PJ, Veltkamp E, Mol JNM: Floral tissue of Petunia hybrida (V30) expresses only one member of the chalcone synthase multigene family. Nucl Acids Res 14: 5229–5239 (1986).
Koezuka Y, Honda G, Sakamoto S, Tabata M: Genetic control of anthocyanin production in Perilla frutescens. Shoyakugaku Zasshi 39: 228–231 (1985).
Kondo T, Tamura H, Yoshida K, Goto T: Structure of malonylshisonin, a genuine pigment in purple leaves of Perilla frutescens ocimoides L. var. crispa Benth. Agric Biol Chem 53: 197–800 (1989).
Kristiansen KN, Rohde W: Structure of the Hordeum vulgare gene encoding dihydroflavonol-4-reductase and molecular analysis of ant18 mutants blocked in flavonoid synthesis. Mol Gen Genet 230: 49–59 (1991).
Kubasek WL, Shirley BW, McKillop A, Goodman HM, Briggs W, Ausubel FM: Regulation of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in germinating Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 4: 1229–1236 (1992).
Leyva A, Jarillo JA, Salinas J, Martinez-Zapater JM: Low temperature induces the accumulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNAs of Arabidopsis thaliana in a light-dependent manner. Plant Physiol 108: 39–46 (1995).
Ludwig SR, Habera LF, Dellaporta SL, Wessler SR: Lc, a member of maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 7092–7096 (1989).
Martin C, Prescott A, Mackay S, Bartlett J, Vrijlandt E: Control of anthocyanin biosynthesis in flowers of Antirrhinum majus. Plant J 1: 37–49 (1991).
Meldgaard M: Expression of chalcone synthase, dihydroflavonol reductase and flavanone-3-hydroxylase in mutants of barley deficient in anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Theor Appl Genet 83: 695–706 (1992).
Moniz de Sa M, Drouin G: Phylogeny and substitution rates of angiosperm actin genes. Mol Biol Evol 13: 1198–1212 (1996).
Murray MG, Thompson WF: Rapid isolation of highmolecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8: 4321–4325 (1980).
Pawlowski K, Kunze R, Vries SD, Bisseling T: Isolation of total, poly(A) and polysomal RNA from plant tissues. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA (eds) Plant Molecular Biology Manual, pp. D5/1–D5/13. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands (1994).
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H: The regulatory C1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homolgy to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activitors. EMBO J 6: 3553–3558 (1987).
Pelletier MK, Shirley BW: A genomic clone encoding flavanone 3-hydroxylase (accession No U33932) from Arabidopsis thaliana (PGR95-080). Plant Physiol 109: 1125 (1995).
Pelletier MK, Shirley BW: Analysis of flavanone 3-hydroxylase in Arabidopsis seedlings. Coordinate regulation with chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase. Plant Physiol 111: 339–345 (1996).
Quattrocchio F, Wing JF, Leppen HTC, Mol JNM, Koes RE: Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 5: 1497–1512 (1993).
Ralston EJ, English JJ, Dooner HK: Sequences of three bronze alleles of maize and correlation with the genetic fine structure. Genetics 119: 185–97 (1988).
Schwarz-Sommer Z, Shepherd N, Tacke E, Gierl A, Rohde W, Leclercq L, Mattes M, Berndtgen R, Peterson PA, Saedler H: Influence of transposable element on the structural and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J 6: 287–294 (1987).
Shirley BW: Flavonoid biosynthesis: ‘new’ functions for an ‘old’ pathway. Trends Plant Sci 1: 377–382 (1996).
Shirley BW, Hanley S, Goodman HM: Effects of ionizing radiation on a plant genome: analysis of two Arabidopsis transparent testa mutations. Plant Cell 4: 333–347 (1992).
Sommer H, Saedler H: Structure of the chalcone synthase gene of Antirrhinum majus. Mol Gen Genet 202: 429–434 (1986).
Sparvoli F, Martin C, Scienza A, Gavazzi G, Tonelli C: Cloning andmolecular analysis of structural genes involved in flavonoid and stilbene biosynthesis in grape (Vitis vinifera L. ). Plant Mol Biol 24: 743–755 (1994).
Tanaka Y, Fukui Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Holton TA, Higgins E, Kusumi T: Molecular cloning and characterization of Rosa hybrida dihydroflavonol 4-reductase gene. Plant Cell Physiol 36: 1023–1031 (1995).
Tanaka Y, Mizutani M, Sakakibara K, Fujiwara H, Fukui Y, Ashikari T, Kusumi T: Molecular cloning of anthocyanin acyltransferase genes (Japanese). In: Abstract book, 15th Annual Meeting of Japanese Society for Plant Cellular Molecular Biology (Kumamoto, July 20–21, 1997), p. 58 (1997).
Tanaka Y, Yonekura K, Fukuchi-Mizutani m, Fukui Y, Fujiwara H, Ashikari T, Kusumi T: Molecular and biochemical characterization of three anthocyanin synthetic enzymes from Gentiana triflora. Plant Cell Physiol 37: 711–716 (1996).
Taylor LP, Briggs WR: Genetic regulation and photocontrol of anthocyanin accumulation in maize seedlings. Plant Cell 2: 115–127 (1990).
Wise RP, Rohde W, Salamini F: Nucleotide sequence of the Bronze-1 homologous gene from Hordeum vulgare. Plant Mol Biol 14: 277–279 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Z., Yamazaki, M., Sugiyama, M. et al. Cloning and molecular analysis of structural genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and expressed in a forma-specific manner in Perilla frutescens. Plant Mol Biol 35, 915–927 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005959203396
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005959203396